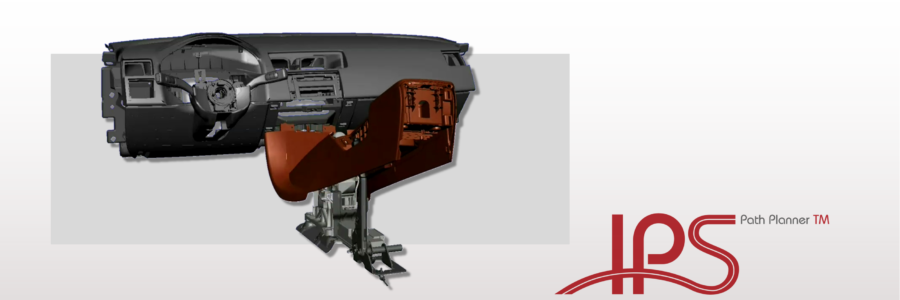
Virtually verifying that products can be assembled and subsequently disassembled for service purposes is an important activity within geometry simulation in the manufacturing industry.
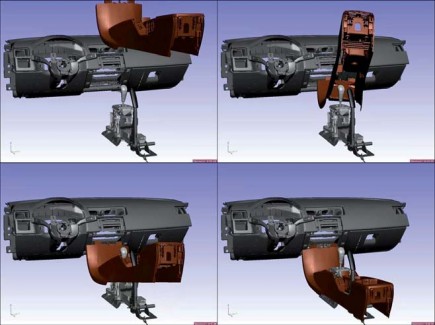
Methods and software for automatically generating collision free assembly paths are therefore of great interest. Also, off-line programming of robots and coordinate measurement machines used in the factory lead to hard problems for the simulation engineer when trying to manually find collision free paths between points, while minimizing cycle time and joint wear.
Despite the use of virtual prototypes in modern industries to replace physical prototypes, the visualization of assembly processes and the programming of industrial robots off-line, the full potential of the virtual factory has not been reached yet. The programming of motions and paths for robots and equipment is still done manually, since the existing support for automatic path planning is very limited. Another limitation is the geometrical accuracy between the virtual model and the physical reality. Therefore, geometrical tolerances need to be considered during path planning. IPS helps taking the first step, going from nominal to production adapted virtual models and hence connecting the production loop including styling, design and manufacturability.
The IPS Path Planner lets simulation engineers import a scene geometry from any CAD system, as a VRML or JT file. Any object in the scene can be set as a so called planning object, which IPS will find an efficient path for, provided that the object can be freely assembled along a path. The calculations done by IPS save the engineer a substantial amount of time, which otherwise would have to be put into manual planning of a collision free assembly path.